core · product
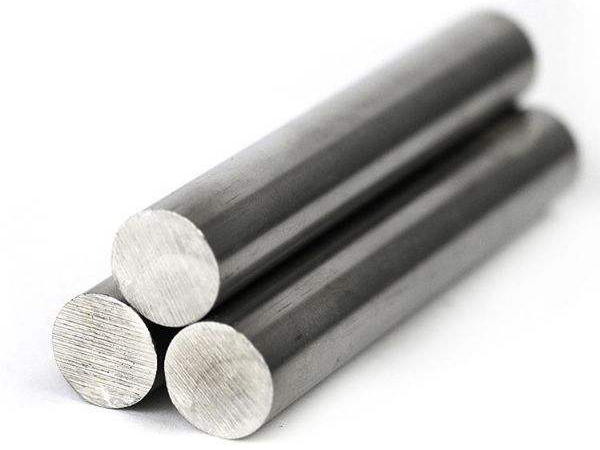
Duplex stainless steel (DSS) refers to stainless steel with ferrite and austenite each accounting for about 50%, and generally requiring at least 30% of the lower phase content. In the case of low C content, the Cr content ranges from 18% to 28%, and the Ni content ranges from 3% to 10%. Some steels also contain alloying elements such as Mo, Cu, Nb, Ti, and N. This type of steel combines the characteristics of austenitic and ferritic stainless steel. Compared with ferrite, it has higher plasticity and toughness, no room temperature brittleness, significantly improved intergranular corrosion resistance and welding performance. At the same time, it also maintains the 475 ℃ brittleness and high thermal conductivity of ferritic stainless steel, with superplasticity and other characteristics. Compared with austenitic stainless steel, it has higher strength and significantly improved resistance to intergranular corrosion and chloride stress corrosion. Dual phase stainless steel has excellent resistance to pitting corrosion and is also a nickel saving stainless steel. Since its birth in the United States in the 1940s, duplex stainless steel has developed to the third generation. Its main feature is that the yield strength can reach 400-550MPa, which is twice that of ordinary stainless steel, so it can save materials and reduce equipment manufacturing costs. In terms of corrosion resistance, especially in harsh media environments (such as seawater with high chloride ion content), the resistance of duplex stainless steel to pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion, stress corrosion, and corrosion fatigue is significantly better than ordinary austenitic stainless steel, and can be comparable to high alloy austenitic stainless steel.