core · product
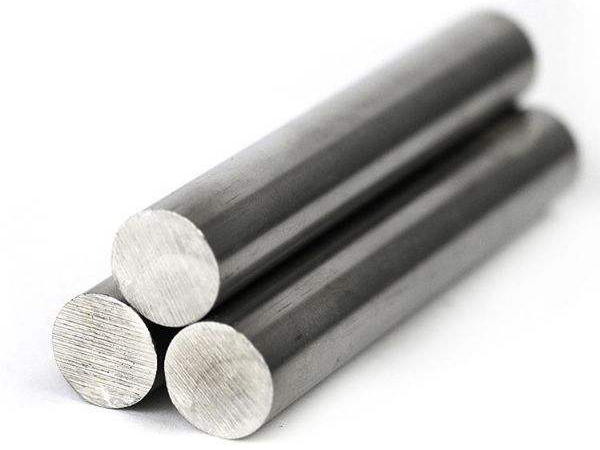
Ultra high strength steel is a type of alloy steel used to manufacture structural components that withstand high stress. Generally, steel with a yield strength greater than 1180MPa and a tensile strength greater than 1380MPa has sufficient toughness, high specific strength and yield ratio, as well as good weldability and formability. According to the degree of alloying and microstructure, it can be divided into three categories: low alloy, medium alloy, and high alloy ultra-high strength steel. As early as the mid-1940s, due to the development of aviation and aerospace technology, in order to reduce the weight of aircraft and improve flight speed, structural materials were required to have higher specific strength. For this reason, Americans changed the heat treatment process on the basis of AISI4130 and 4340 steel, using quenching and low-temperature tempering to obtain a tempered martensitic structure, which increased the tensile strength of the steel to over 1600MPa. Used for manufacturing aircraft structural components, significant results have been achieved in reducing the weight of aircraft. After the 1950s, new progress was continuously made in improving the strength and toughness of steel, and ultra-high strength steels such as 300M, D6AC, and H-11 were successfully developed. In 1960, International Nickel Corporation of the United States developed martensitic aging steel and gradually formed the 18Ni martensitic aging steel series, with yield strengths of 1400MPa, 1700MPa, 2100MPa, and 2400MPa, respectively, and its fracture toughness reached a high level. After the 1970s, the development of ultra-high strength steel mainly focused on improving toughness. After the 9NiCo series, the United States successfully developed AF1410 secondary hardening ultra-high strength steel based on Hy180 steel. This steel adopts low-carbon martensite and precipitation alloy carbide dispersion strengthening effect, which not only has high strength and toughness, but also has high stress corrosion resistance. It has been used to manufacture important structural components such as aircraft landing gears and tail shafts, and has received attention and favor from the aviation and aerospace sectors. Since the 1990s, in order to meet the needs of the aviation industry, the United States has successfully developed AerMet100 based on AF1410 steel. The steel has a tensile strength of 1965 MPa and a fracture toughness of 120 MN · m, with good stress corrosion resistance. Used for manufacturing aircraft landing gear, it will greatly improve flight safety and reliability, and extend the service life of the aircraft.