core · product
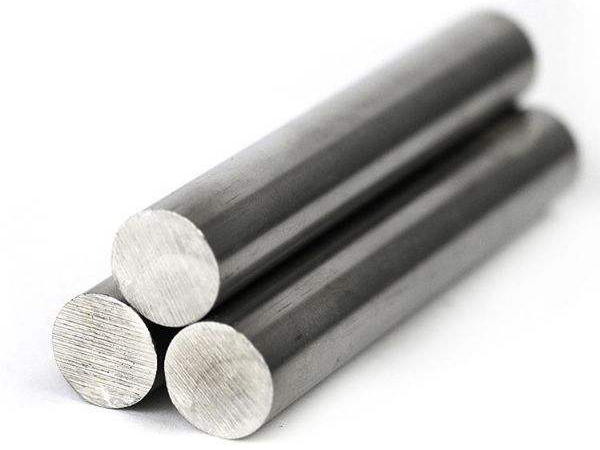
300 series stainless steel, also known as 18-8 steel, is the most commonly used material for fasteners, joints, pipes, and pipelines. 304 stainless steel is the most common material for stainless steel fasteners. 18-8 steel is the nominal content of chromium and nickel in 300 series stainless steel. These materials appear to have good corrosion resistance on the surface, but heating 304 stainless steel to above 850 ° F (about 199 ° C) will reduce the chromium content due to the deposition of carbon. At high temperatures, chromium combines with carbon to form chromium carbide, which is not rust resistant. The use of 304L stainless steel can alleviate this problem, as the carbon content of 304L stainless steel is one-third of that of 304 type stainless steel. The formation of chromium carbide can be eliminated by using 321 stainless steel or 347 stainless steel. 321 stainless steel and 347 stainless steel contain titanium and niobium respectively, and their properties are very stable. Due to the higher affinity of titanium and niobium for carbon compared to chromium, they form titanium carbide and niobium carbide respectively with carbon at high temperatures, thus retaining chromium. Due to the fact that the strength of 300 series stainless steel is only strengthened during cold forming, when the temperature reaches 1000 ° F (approximately 283 ° C), thermal cycling will cause the fastener strength to decrease to the annealed state. If the decrease in strength is unacceptable, then stable materials 321 or 347 are also unsatisfactory. Therefore, other materials should be considered.