core · product
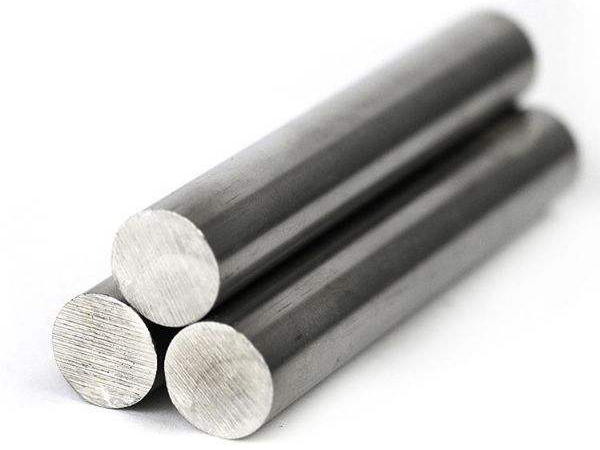
400 series stainless steel is an alloy of iron, carbon, and chromium. This type of stainless steel has a martensitic and ferritic structure, thus possessing normal magnetic properties. 400 series stainless steel has strong resistance to high-temperature oxidation, and compared with carbon steel, its physical and mechanical properties have been further improved. Most 400 series stainless steels can undergo heat treatment. The chromium content of the 400 series stainless steel is lower than that of the 300 series stainless steel, but there is no carbon deposition problem like the 300 series, and it can be heat treated and used in working environments with temperatures up to 1200 ° F (about 393 ℃). However, due to the chromium content being only 12%~14%, it will corrode when used in environments with severe chemical atmospheres, while the 300 series contains 16%~20% chromium and will not corrode. 300 series stainless steel and 400 series stainless steel have the same strength. 300 series stainless steel is non-magnetic, while 400 series stainless steel has magnetism. Among the commonly used 400 series stainless steel varieties, there are 430 stainless steel models with 18% chromium and 410 and 420 stainless steel models with 13% chromium. Among them, 430 stainless steel model is the most commonly used. The characteristics of the 430 stainless steel model are that it is inexpensive, has a small coefficient of thermal expansion, and has better resistance to chloride stress corrosion than the 300 series stainless steel variety; However, its shortcomings are that its formability, weldability, and tensile strength are lower than those of 304 type stainless steel models, so its application field is limited. Under the same chromium content, such as in oxidizing media such as atmosphere, fresh water, and nitric acid, the corrosion resistance of 400 series stainless steel varieties is the same as that of 300 series stainless steel varieties, and usually the corrosion resistance of 400 series stainless steel varieties is better than that of 200 series stainless steel varieties. The addition of trace amounts of niobium, titanium, copper, and aluminum to the 400 series stainless steel varieties can improve their deep drawing performance, weldability, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature strength, and can partially replace the 304 type stainless steel model.